Taste buds contain the receptors for taste. They are located around the small structures on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus and epiglottis, which are called papillae. These structures are involved in detecting the five (known) elements of taste perception: salty, sour, bitter, sweet, and umami. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nerves. Continue reading
Monthly Archives: December 2011
Dental Treatments to Avoid When You Are Pregnant Part 2
Continued from Part 1
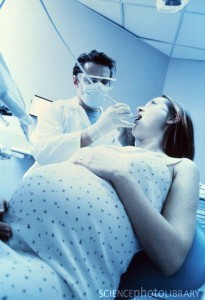
Dental treatment is best carried out during the second trimester, but advanced restorative procedures are probably best postponed until the state of the gums improves after giving birth and prolonged sessions of treatment are better tolerated. In the second and third trimesters the fetus is growing and maturing but can still be affected by infections, drugs and possibly other factors. In the third trimester the supine hypotension syndrome may result if the pregnant woman is laid flat. The person should therefore be put on one side to allow blood return to recover. Some pregnant women also have a hypersensitive gag reflex. Elective dental care should be avoided in the last month of pregnancy, as it is uncomfortable for the patient. Moreover premature labor or even abortion may also be attributed, without justification, to dental treatment. Continue reading
What is Obturation in Root Canal Therapy? Part 2
According to Grossman
-Lateral condensation method
-Vertical condensation method
-Sectional method
-Compaction method (mcSpadden)
-Metal-core obturation
-Silver-cone method
-Stainless steel file method
-Chemically plasticized gutta-percha
-Injection techniques of obturating canals
-Hydron
-Thermo-plasticized gutta-percha method
-Obtura II, Ultrafil
White sponge naevus
White sponge nevus (WSN), also known as Cannon’s disease, Hereditary leukokeratosis of mucosa and White sponge nevus of Cannon, is an autosomal dominant skin condition. Although congenital in most cases, it can first occur in childhood or adolescence. Continue reading
Dental Treatments to Avoid When You Are Pregnant Part 1
Pregnancy is a major event in any woman’s life and is associated with physiological changes affecting especially the endocrine, heart and blood systems and often attitude, mood or behavior. Therefore pregnant women should take extra care during this period to avoid any circumstances that could harm their fetuses, including certain dental treatments. Continue reading
Removable orthodontic appliances
Orthodontic treatment can be divided into:
i) Removable orthodontic appliances
ii) Fixed appliances (braces)
iii) Orthognatic surgery
We will be focusing on removable orthodontic appliances in this article.
Firstly, you may want to know what are the types of movement involved in orthodontics and the amount of force required for that movement of a single tooth: Continue reading
What is Obturation in Root Canal Therapy? Part 1
The first visit to the dentist, the dentist will gives you local anaesthesia and remove all the pulp tissue. He will then put a temporary filling material to fill up the empty spaces. This process is called Access Opening. During the second visit, the temporary filling material is removed and root canal material like gutta percha is placed. A temporary filling material is placed again. This process is called Obturation. During your last visit, the temoporary filling material is removed and replaced by permanent filling material like composite/amalgam and a crown preparation is done.
Early Childhood Caries (ECC)
What is it?
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) is a chronic and infectious oral disease of young children, most commonly seen in poor and minority populations.
The American Dental Association (ADA) defines ECC as “the presence of one or more decayed (non-cavitated or cavitated lesions), missing (due to caries) or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth in a preschool-age child between birth and 71 months of ageâ€. Continue reading
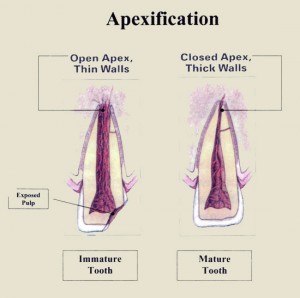
Apexification
Definition:
Apexification is a method to induce development of the root apex of an immature, pulp less tooth by formation of osteocementum or other bone-like tissue. It differs from apexogenesis, the physiologic process of root development.
Cherubism Part 2
Anatomy
Cherubism is displayed with genetic conformation and when excessive osteoclasts are found in the affected areas of the mandible and Maxilla. Large cysts will be present with excessive fibrous areas inside the bone. The fibers and cysts will be found among the trabecula of the Coronoid process, the ramus of mandible, the body of mandible and the maxilla regions. The maxilla will be affected up to and including the orbits and sometimes inside the lower orbits. The maxilla and zygomatic bones are depressed and eyes appear to gaze upward. The maxilla has been found to be more severely affected in most cases than the mandible bone. Some patients found with lower inner orbital growths and cysts may lose vision. Continue reading