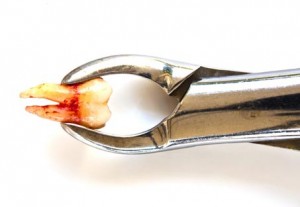
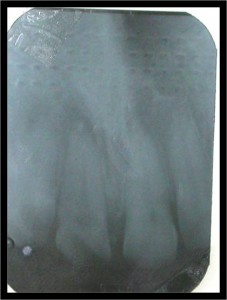
Tooth extractions can be a bloody affair. Bleeding or the abnormal flow of blood is normally seen in tooth extraction but excessive bleeding can be caused by something as simple as taking aspirin to prevent heart attacks or because of some inherited blood disorders. Continue reading
Monthly Archives: December 2011
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 2
BUCCAL BIFURCATION CYST
SYNONYMS
Mandibular infected buccal cyst,
Paradental Cyst,
Inflammatory collateral dental cyst
Inflammatory lateral periodontal cyst
Craig’s cyst
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 1
Definition
A cyst is a pathological cavity in hard and soft tissues having fluid or semi-fluid or gaseous contents, that are not created by the accumulation of pus frequently, but not always lined by epithelium.
Continue reading
Thyroglossal duct cyst
A thyroglossal cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct.
Presentation
It usually presents as a midline neck lump (in the region of the hyoid bone) that is usually painless, smooth and cystic, if infected pain can occur. There may be difficulty breathing, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), and/or dyspepsia (discomfort in the upper abdomen), especially if the lump becomes large. Continue reading
Crowns for children
 Intoduction to crowns for children
Intoduction to crowns for children
Just as we have crowns in adult dentition, so we have crowns for children. These crowns differ from those in adults in many ways, as will be discussed in the following sections. When your child has caries in his or her teeth, restorations with fillings such as composite or even amalgam is sufficient for small cavities, but if the cavity has become so large to an extent that normal restorations will be weak and easily fracture, a crown becomes the better option to protect the tooth from further damage. Continue reading
Radiographic Faults and Artifacts Part 2
Lymphoepithelial cyst
The oral lymphoepithelial cyst develops within a benign lymphoid aggregate or accessory tonsil of the oral or pharyngeal mucosa. The surface of such aggregates may be indented with tonsillar crypts, as are the much larger pharyngeal tonsils of the lateral pharyngeal walls. The crypts may become obstructed by keratin or other debris, or the surface opening may become constricted during episodes of inflammatory hyperplastic responses. Certain cases develop a complete disunion of the crypt epithelium from the surface epithelium, resulting in a subepithelial cyst lined by the old crypt epithelium. This cyst was first reported by Parmentier in 1857 as hydatid cyst. Outside of the head and neck region, lymphoepithelial cyst is found most frequently in the pancreas and testis. Continue reading
Radiographic Faults and Artifacts Part 1
THE IDEAL RADIOGRAPH IS THE ONE WHICH SHOWS:
1. Optimum density
2. Optimum contrast
3. Accurate
4. Covers the area of interest completely
When any of the above conditions are not satisfied it may be termed as the faulty radiographs.
Working Length Determination in Root Canal Treatment Part 2
Tear drop silicone – rubber stops have an added advantage because they do not have to be removed form the instrument during sterilization at 4500 F and tear drop tip can be positioned to indicate instrumental curvature
Rubber stops instruments have certain disadvantages like movement of up (or) down the shaft, leading to short (or) past the apical constriction and time consuming.
Dyskeratosis follicularis and its oral manifestations
Darier’s disease, also known as keratosis follicularis or dyskeratosis follicularis, is a rare disorder of keratinization. It is an autosomal dominant genodermatosis with high penetrance and variable expressivity. Its manifestation appears as hyperkeratotic papules primarily affecting seborrheic areas on the head, neck, thorax, and less frequently the oral mucosa. Continue reading