Continued from Part 1
Drug reactions
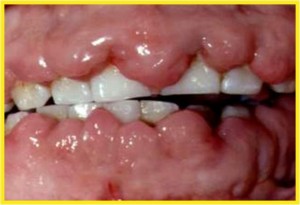
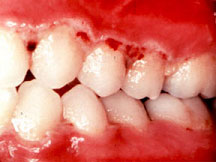
- Epanutin/phenytoin/dilantin/DPH – an anticonvulsant drug given to epileptics, some degree of gums enlargement occurs in a large percentage of epileptics taking phenytoin, especially in those under 40 years of age.
- Cyclosporine – an immunosuppressive drug, it can produce fibrous hyperplasia of the gums. The condition is however less common in patients on cyclosporine, but when it occurs it may be very severe.
- Nifedipine – a calcium channel blocking drug given to treat cardiac angina, arrhythmias and hypertension, it produces fibrous hyperplasia of the gums. Nifedipine hyperplasia is less firm than the other two, and contains a higher proportion of ground substance. Continue reading