Once you enter the dental clinic, you will see a dental chair :
When you sit down in a dental chair, your eye first goes to the row of shiny, sharp instruments sitting in front of you. : Continue reading
Once you enter the dental clinic, you will see a dental chair :
When you sit down in a dental chair, your eye first goes to the row of shiny, sharp instruments sitting in front of you. : Continue reading
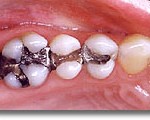 Dental restorations are placed to restore the function, anatomy and integrity of tooth structure which can be lost due to various reasons such as dental caries, trauma and etc. They can be broadly classified into two categories: direct and indirect restorations. Direct filling materials are used for chair side restorations where as indirect restorations such as crowns, bridges, inlays are fabricated outside the patient’s mouth. Before we venture into the pros and cons of different types of restorative materials, let me explain to you the requirements of an ideal dental filling material. Continue reading
Dental restorations are placed to restore the function, anatomy and integrity of tooth structure which can be lost due to various reasons such as dental caries, trauma and etc. They can be broadly classified into two categories: direct and indirect restorations. Direct filling materials are used for chair side restorations where as indirect restorations such as crowns, bridges, inlays are fabricated outside the patient’s mouth. Before we venture into the pros and cons of different types of restorative materials, let me explain to you the requirements of an ideal dental filling material. Continue reading
Dental scrap gold is fast becoming an additional resource for people wishing to sell gold. Dental scrap gold consists of any gold that has been used in the mouth and is worth more sold than kept. It can include any failed, damaged or deteriorated gold or silver crowns, any bridges, PFM’s (porcelain fused to metal), PFG’s (porcelain fused to gold), Inlays, Gold Partials and more. In fact here is a list of the dental scrap including gold, silver and platinum that can be sold, and these can be with or without bone or porcelain: Continue reading
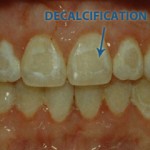
Decalcification simply means loss of calcium from teeth.
Bacteria found in dental plaque will convert carbohydrate and sugars into acids. This acidic condition will cause minerals to leach out from enamel. It is also known as decalcification. High-sugar diets, lack of good oral hygiene practices are the main factors that contribute to decalcification of tooth enamel. Continue reading
The process of using ceramic materials to replace or repair teeth is not new. According to the Indiana University School of Dentistry, the first porcelain denture tooth was introduced in 1789. Of the materials used today for tooth restoration, ceramic porcelain comes closest to duplicating the color and translucency of natural teeth. Ceramic teeth are, however, more expensive than other materials and can add up to a major investment. Protect your investment and help your ceramic teeth last longer by cleaning them properly. Continue reading
Amalgam was first introduced in United States during 1833. It is then used widely as dental filling material over the years because of its strength, durability and low cost (especially for posterior teeth). It is now discontinued or banned in certain countries such as Norway, Sweden, Denmark because of its known biological effects on human body. Amalgam is made of metals such as Silver, Tin, Copper, Zinc and Mercury. 50% of amalgam is made of mercury and they are then mixed to form a hard material which has silvery grey appearance through a process which is known as amalgamation. Patients are exposed to high dose of mercury during the process of placing and removal of amalgam restoration. Continue reading
Parents or guardians play an important role in regard to a child’s diet and oral health habits. Newly emerged teeth are particularly vulnerable to dental decay. As teeth gets older and become more mature, the outer surface becomes harder and more resistant to acid attack.
Teeth are constantly being attacked by acid produced by plaque bacteria as well as acidic foods and drinks. Acids cause damage below the tooth surface, causing microscopic holes in the tooth. If the acid damage continues over a period of time, the tooth becomes so fragile that a hole becomes visible in the tooth. As the hole gets bigger, the tooth will need a filling. However dental sealants can be placed on your child’s teeth to prevent tooth decay from occurring if risk of decay is detected early. Continue reading
What is a dental filling?
A dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the physical integrity of the intended restorative material.
Dental fillings can be divided into three broad types: Continue reading
Composite resin and amalgam are the most commonly used filling materials in dentistry. Throughout the years, the content of both materials have been modified to improve the quality of the fillings.
Dental composite resins are types of synthetic resins. A composite material is a product which consists of two distinct phases normally formed by blending together components having different structures and properties.The purpose of this is to produce a material having properties which could not be achieved from any of the individual components alone. The two main components of composite filling materials are resin phase and the reinforcing filler. The resin gives the material the ability to be moulded at ambient temperature and polymerization achieved in a short time.Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, aesthetic, and insensitive to dehydration and were inexpensive. It is easy to manipulate them as well. Composite resins are most commonly composed of Bis-GMA monomers, a filler material such as silica and in most current applications, a photoinitiator. Dimethacrylates are also commonly added to achieve certain physical properties such as flowability. Further modification of its physical properties is achieved by changing the concentrations of each constituent.Unlike amalgam which essentially just fills a hole, composite cavity restorations when used with dentine and enamel bonding techniques restore the tooth back to near its original physical integrity.
The main advantage of dental composite over amalgam is improved aesthetics. Composite is a tooth coloured material and it comes in a wide range of tooth colours allowing near invisible restoration of teeth. Composite is bonded to the tooth with the use of dentine bonding agent. This strengthens the tooth structure. Unlike amalgam, there is no need to create retentive features which destroys healthy tooth structure because composite bonds to tooth chemically. Therefore, using composite material as filling is proven more conservative and less tooth preparation is needed. Continue reading
What is a  dental filling?
A tooth consists of enamel,dentine, pulp and cementum. Enamel is the outermost layer which forms the crown of a tooth. Tooth surface is covered by a bacterial biofilm,known as plaque. The bacteria metabolizes sugar and releases acid which destroys the enamel. This process is called decay or dental caries. When oral hygiene is inadequate, dental decay progresses into the dentine layer and in later stage, into the pulp. Decayed tooth is weak and brittle, thus it becomes soft, forming what is called cavity. A tooth damaged by decay needs to be filled to restore its normal function, shape and strength. Continue reading