Gum disease is not limited to adults. Periodontitis (inflammation of the supporting tissues of the teeth or also known as the periodontium) can also occur in young people. Periodontal disease can generally be divided into different types including chronic, aggressive and necrotizing periodontal disease; with aggressive periodontitis commonly seen in the younger age group.
What is aggressive periodontitis?
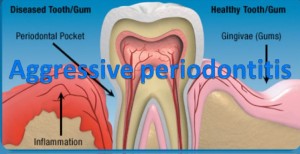
Aggressive periodontitis, also referred to as early onset periodontitis, often occurs in young people. This condition used to be called juvenile periodontitis. It can be subdivided according to whether it begins before or after puberty. Aggressive periodontitis is distinct in its clinical features and its bacteriological, whereby 70% of the microflora involved consists of the bacteria Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.
Periodontitis that occurs before puberty is very rare. It begins with the eruption of primary teeth in the first year and causes severe inflammation with bone and tooth loss.
There are two main forms of aggressive periodontitis:
- Generalized aggressive periodontitis (GAP), previously generalized juvenile periodontitis
- Localized aggressive periodontitis (LAP), previously localized juvenile periodontitis
GAP is a severe form of generalized periodontitis affecting young adults (less than 30 years of age). Generalized connective tissue attachment loss between teeth is seen affecting at least three permanent teeth other than the first molars and front teeth. There is pronounced episodic nature of destruction of tissue attachment and jaw bone with tooth loss possible within a year of onset. This condition affects 1-2% of the western population with an increase risk in Afro-Caribbeans.
LAP is a severe form of localized periodontitis with onset around puberty. Localized attachment loss of at least two permanent teeth is seen; one of which is a first molar and involving no more than two teeth other than first molars and incisors.
If the condition is localized and treated, the prognosis is positive. Individuals with severe and widespread aggressive periodontitis are at high risk for tooth loss.
What is the difference between chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis?
Chronic periodontitis can appear at any age but is most prevalent in adults. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the supporting structures of the teeth and loss of gum attachment due to destruction of the periodontal tissues. Prevalence and severity of the disease increase with age.
Who is more likely to get aggressive periodontitis?
This condition occurs in 1 in 1000 adolescents whereby it is common in the West African region and low socioeconomic groups. Aggressive periodontitis varies among different ethnic groups.
The age of presentation of aggressive peridontitis is usually adolescents more than 12 years of age, and sometimes younger age groups. This condition is more common in females, in which the risk is 2 to 10 times greater than males.
Aggressive periodontitis is a genetic condition whereby the condition can be inherited in the family. This condition has no relationship with any systemic conditions but it is associated with Papillon-Lefevre syndrome that has characteristic features of thickened skin on the soles and palms, calcifications within the skull and aggressive periodontitis.
Signs and symptoms of aggressive periodontitis
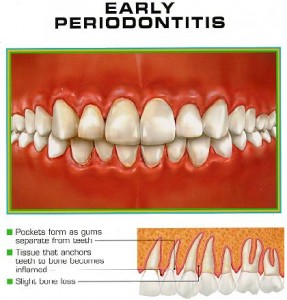
- Gums may show few signs of inflammation, if any
- Little or no plaque and tartar seen
- Tartar deposits beneath the gumline are usually absent
- Because of absence of clinical inflammation, condition may go undetected till of advanced stage
- Mobility and drifting of tooth, initially the front teeth and 1st molars
- Pocketing of gums and tissue attachment loss rapidly increases with no local factors involved
- Bone destruction initially localized to the front teeth and 1st molars
- Vertical bone loss that is symmetrical, like a mirror image
- Teeth may be lost in 4 to 5 years (generalized aggressive periodontitis)
Aggressive periodontitis treatment
Early diagnosis is important as the chances of saving teeth s better when attachment loss is significantly less.
Treatment plan
- Samples of microflora beneath the gumline is taken for microbiological investigation for antibiotic sensitivity
- Oral hygiene instruction and counseling is given about the nature of condition, responsibility, of the individual to abide to the high level of home care
- Administration of antibiotics
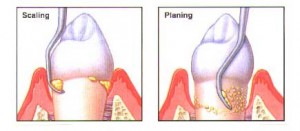
- Scaling and root planing of affected sites
- Extraction of involved teeth when necessary especially those of hopeless prognosis with excessive bone loss and drifting
- Periodontal surgery depending on clinical picture, for example gum flap surgery, root amputation and bone graft
- Bite adjustments with selective grinding for teeth drifted into premature contacts or gentle orthodontic treatment for drifted incisors
- Prosthesis for missing teeth
- Maintenance recall every 3 months for oral hygiene reinforcement and scaling, sample testing of microflora to monitor bacteria and appropriate antibiotics
How to prevent aggressive periodontitis
Unfortunately aggressive periodontitis is a condition related to genetics hence it cannot be prevented. Â Therefore it is important to make regular appointments with your dentist to ensure that this condition is detected and treated early for a good prognosis.