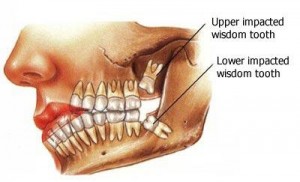
Wisdom teeth are a frequent problem for most people. Being the last tooth to develop and emerge from the mouth (normally between 18 to 24 years of age), wisdom teeth tend to have not enough room to erupt in the jaws which can cause them to be impacted.
An impacted tooth means that the path of eruption of the tooth is blocked by another tooth or bone which therefore prevents it from assuming a normal position in the mouth. Wisdom tooth impaction is not a disease but is considered an abnormal state.
Complications of wisdom tooth
Impacted wisdom tooth can lead to:
- Pericoronitis (inflammation of soft tissues around the crown of a partially erupted tooth, most commonly seen in association with the lower wisdom teeth)
- Tooth decay
- Bone loss in the region of the wisdom tooth
- Gum disease problems
- Cysts and tumors may arise
- Crowding of teeth
When to remove wisdom tooth
- Tooth decay that cannot be restored
- To facilitate placement of orthodontic appliance or prosthesis
- In presence of pus or severe pain
- Resorption of the tooth or adjacent teeth
- Fracture of wisdom tooth
- Related to a cyst or tumor
- Tooth/teeth preventing jaw reconstruction surgery
- Satisfactory tooth for use as donor for transplantation
Surgical removal of wisdom tooth in absence of any disease is not usually indicated. However it should be monitored from time to time by clinical examination and radiographs.
Causes of wisdom tooth nerve pain
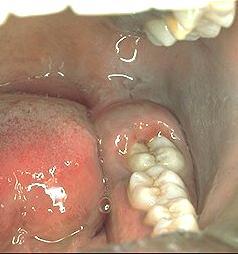
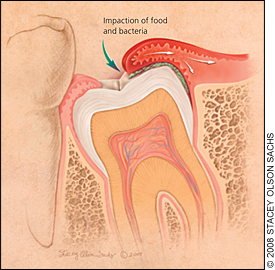
The space between the crown of the tooth and the overlying gum flap (operculum) is an ideal area for the collection of bacterial plaque and food debris, leading to inflammation (pericoronitis).
Swelling from the inflammation increases the chance of trauma from the opposing teeth and aggravates the inflammation. Wisdom tooth pericoronitis is often a recurrent problem if the main cause is not removed.
Wisdom tooth infection can also occur when the tooth is partially erupted and there is poor oral hygiene. Bacteria can cause decay of the tooth and lead to inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding the tooth.
Wisdom tooth inflammation (pericoronitis) symptoms
The usual wisdom tooth symptoms are:
- Localized wisdom teeth pain and discomfort
- Swelling, redness and soreness in the gum flap
- Bad taste associated with persistent oozing of pus from beneath the gum flap
- Bad breath
- Limitation in opening the mouth
- Discomfort on swallowing
- Evidence of trauma by opposing tooth/teeth
How to relieve pain from wisdom tooth
For temporary relief of pain before your visit to the dentist, you can try:
- Taking mild pain killers.
- Rinsing your mouth with salt water or saline solution mouthwash by adding a pinch of salt in lukewarm water and gargling with it.
- Placing a drop of clove oil directly on the crown of the affected tooth and dab another drop on the gum around the tooth to ease toothache pain until you can see your dentist. You can buy over-the-counter preparations of clove oil and the oil is placed directly on tooth, not ingested.
- Mixing ½ teaspoon of goldenseal powder, 1 drop of clove bud essential oil and 2 drops of chamomile essential oil with a few drops of water until a thick paste forms. It combines the pain-fighting components in clove bud oil with the infection-fighting ingredients in both chamomile and goldenseal. Dab into the affected area with a cotton-tipped swab. Apply not more than four times per day until you can see your dentist.
Treatment of wisdom tooth pericoronitis
In the acute phase:
- Initial treatment is aimed at resolving the symptoms. Food debris in the infected area will be removed from under the gum flap by gentle flushing with warm water or dilute hydrogen peroxide. Any dead tissues will be removed under anesthetic agent applied to the tissue.
- Removal of opposing tooth/teeth if traumatic bite present.
- Use of appropriate pain killers.
- Use of appropriate antibiotics in the presence of severe local disease or if systemic symptoms identified (fever, swelling in the neck and body discomfort).
- Improving oral hygiene, resting at home, keeping the mouth clean using warm saltwater mouthwash and drink fluids to avoid dehydration.
- Use of 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthwash.
Following resolution of the acute phase:
- Local soft tissue surgery (operculectomy)
- Removal of associated tooth
Possible complications from wisdom tooth removal
- Swelling and pain after wisdom tooth extraction
- Bleeding after surgery
- Damage to nerves around the region
- Damage to the neighboring teeth
- Damage to the gum tissues
- Fracture of jaw bone
- Dry socket
When to contact your dentist
Contact your dentist when you show the following symptoms:
- Extreme pain at the back of the mouth
- Redness and swelling in the wisdom tooth area
- Swelling of the cheek