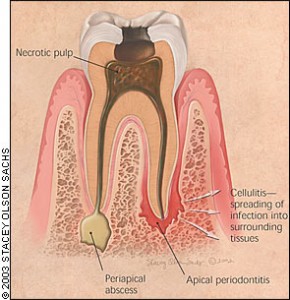
ACUTE PERIODONTAL ABSCESS
Pain and swelling
It is usually mistaken for acute alveolar abscess
It may occur with vital or necrosed pulp, but its origin is
usually an exacerbation of infection with pus formation
in an existing deep infra bony pocket.
If pulp is vital, Rx is Curettage
debridement
establishment of drainage through sulcular crevice
Pulp – non vital : Root Canal Treatment
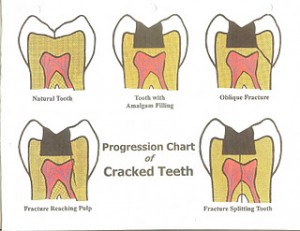
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME
DEFINITION:
Incomplete fractures through the body of the tooth may cause pain of apparently idiopathic origin and this is referred to as cracked tooth syndrome.
The patient usually complains of pain ranging from mild to excruciating at the initiation or release of biting pressure
Diagnosis
By reproducing the pain.
When the patient bites on cotton applicator or rubber wheel, fracture segments may separate and the pain may be produced at the initiation or release of biting pressure.
By Transillumination
Use of dyes.
Rx
– Immediate reduction of offending cusps by
selective grinding
– If dentine is exposed, sedative cement is placed
and a stainless steel band is cemented.
– Definitive Rx – to preserve vital pulp by full crown
– Irreversible pulpitis – Root Canal Treatment
CROWN FRACTURE:
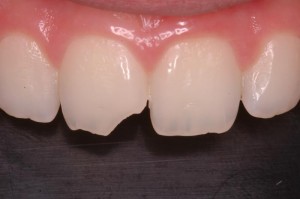
Vertical fracture Poor prognosis
Horizontal fracture ————Enamel Fracture
Enamel and Dentine Fracture
Enamel, Dentine Fracture
involving pulp
DIAGNOSIS
Transillumination
Wedge test
Dye test
Radiographs
TREATMENT
Enamel fracture ——- composite
Enamel and Dentin without pulp—-sandwich technique
Enamel and Dentin with pulp exposure —pulpotomy
—–R.C.T
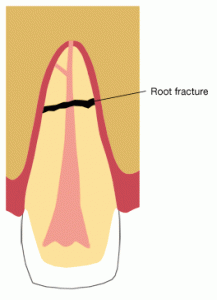
ROOT FRACTURE:
Prognosis depends on location and direction of fracture
A horizontal fracture above the alveolar crest has
excellent prognosis since the tooth can be restored .
Apical root fracture has favourable prognosis
Rx for horizontal fracture – Stabilization by ligation of tooth with
Adjacent teeth if mobility is present
Pulp is in a state of shock so vitality tests to be repeated after 6wks
Cervical 1/3 fracture – Re attachment of the segment if displaced
Stabilization by splinting
If the segment is lost, post and core is done Prognosis is favourable
Middle 1/3 fracture
Is treated by stabilization and orthodontic
extrusion of fractured segment
Prognosis is poor
Apical 1/3 fracture is left untreated
Prognosis is very good
Vertical fracture of root has hopeless prognosis.
Emergency Rx is extraction
In multirooted teeth, hemisection is done.
REFERRED PAIN:-
Cause: Pulpo periapical pathosis
Dental pain can have its origin in trigeminal neuralgia,
atypical facial neuralgia ,migraine,cardiac pain,TM arthrosis
Sinusitis –may cause pain in upper molars
Periodontal pain is mistaken as periapical
Otitis media can refer pain to mandibular molars
Tooth ache on left side can be due to MI or angina
Pain from lower posterior teeth can be referred to ear
or back of head
Rx depends on diagnosis
AVULSION:
DEFINITION:
It is defined as complete displacement of the tooth from the alveolus .
It is usually the result of trauma to an anterior teeth and is both dental and emotional problem.
Prognosis depends on the amount of time the tooth is out of the socket.
Management:
Outside the dental office.
Success depends on speed with which the teeth is replaced.
Extra oral time:
Should not exceed 30 minutes ,should be placed within 15-20 mins. Care should be taken not to damage the attachment apparatus.
Management:
Outside the dental office.
Success depends on speed with which the
teeth is replaced.
Instructions:
Tooth should be held by the crown,
Root is washed gently in running water or saline, and
gently placed in the socket
Patient is brought to dental office.
If the teeth cannot be placed in the socket ,
It should be stored in appropriate media.
Suggested Media:
Vestibule of mouth, Physiologic saline, Milk
Cell culture media, Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution
[HBSS]
Milk
is considered the best medium because it has pH & osmolality compatible to vital cells and relatively free of bacteria and is readily available.
It maintains vitality of periodontal tissues for 3 hours.
Water
tooth should not be kept in water since it is a
hypotonic environment and leads to rapid cell lysis.
Management at the office
If the tooth was replanted ,positioning in the socket is assessed and Rg is taken for confirmation
If unacceptable, tooth is removed gently and replanted Splinting and soft tissue management is done.
Preparation of root:
– If extra oral time is < 20 mins, periodontal healing is excellent. – Root is rinsed of debris with water or saline and replanted gently Rx prognosis depends on whether root is open or closed. – If extra oral time is > 60 mins. periodontal cells have died, then the tooth is soaked in citric acid for 5 mins, in 2% SnF for 5mins to remove remaining periodontal cells and replanted.
– If tooth is dry for more than 60mins ,endodontic Rx is is
Performed extra orally. The socket is lightly aspirated if blood clot is present.
Splinting : to be done for 7-10 days
the splint should allow physiologic tooth movement
during healing to prevent ankylosis .
after splinting, traumatic occlusion is avoided .
After 7-10 days splint is removed, since 1 wk is sufficient to
create periodontal support.
In case of alveolar fracture ,splint is placed for 4-8 wks.
Management of soft tissues is done .
Adjunctive therapy:
analgesics and antibiotics to prevent infection
chlorhexidine rinse
Endodontic Rx is initiated if the tooth is nonvital
In cases of open apex apexification is done
Follow up care to be done every 6mths for 5 years.
Prognosis:
The failure of replantations is related to resorption
The extra oral time is very crucial and affects the treatment results
When teeth were replanted within 30mins only 10% showed resorption where as 95% resorbed when replanted more than 2hrs post trauma
Endodontic flare ups or mid Rx emergencies:
DEFINITION:
It is defined as an acute exacerbation of peri radicular pathosis after the initiation or continuation of RCT
Causes:
Inadequate debridement [residual pulp tissue]
Debris extrusion during canal preparation.The necrotic ts , micro organisms, dentin filings, pulp tissue fragments may extrude periapically.
Over instrumentation may induce inflammatory response apically
Inadequate sterilization.
Irrigating solutions and intra canal medicaments
Over filling — extrusion of sealer or G.P or both
ZnOE sealer may induce chronic inflammation
Un traced root canal
Re treatment cases have higher incidence due to associate periapical pathosis
Associated with peri apical lesion.
Host factors—post operative pain depends on intensity of
Pre operative pain and patient apprehension
TREATMENT:
Patient should be relaxed during the Rx.
Usually post-operative pain decreases with in 72 hrs.
Flare ups can be reduced by complete cleaning and shaping during initial visit.
Ca(OH)2 dressing to prevent or treat flare ups.
Occlusal reduction
If necessary antibiotics and analgesics.