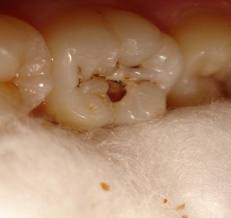
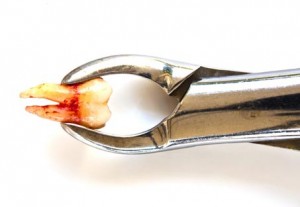
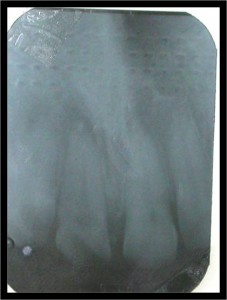
When caries in your child’s teeth has gone so deep that it has reached, or is near the pulp, your child will need more than just a normal filling to restore the tooth. If the infection from caries has reached the pulp, yet left untreated, the infection may spread causing more harm to your child. The pulp therapy that can be done on your child’s teeth can be divided into vital and non-vital technique:
Mental nerve
Mental nerve is a general somatic afferent (sensory) nerve which provides sensation to the anterior aspects of the chin and lower lip as well as the buccal gingivae of the mandibular anterior teeth and the premolars. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, which is itself a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). The nerve emerges at the mental foramen in the mandibula, and divides beneath the Depressor anguli oris muscle into three branches: Continue reading
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 3 and Scintigraphy
Nonodontogenic Cysts
NASOPALATINE DUCT CYST
Synonyms
Nasopalatine canal cyst
Incisive canal cyst
Nasopalatine cyst
Median palatine cyst
Median anterior maxillary cyst
Pros & Cons of Tooth Extractions
When faced with an aching tooth, the first thing that comes to mind is to pull the miserable tooth out. However depending on the cause of the toothache, tooth extraction is not the only way out of the pain. There are many causes of toothache and there is a chance that the aching tooth could be saved. Continue reading
How to Quickly Stop Bleeding from Tooth Extraction
Tooth extractions can be a bloody affair. Bleeding or the abnormal flow of blood is normally seen in tooth extraction but excessive bleeding can be caused by something as simple as taking aspirin to prevent heart attacks or because of some inherited blood disorders. Continue reading
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 2
BUCCAL BIFURCATION CYST
SYNONYMS
Mandibular infected buccal cyst,
Paradental Cyst,
Inflammatory collateral dental cyst
Inflammatory lateral periodontal cyst
Craig’s cyst
Radiographic Appearance of Cysts Part 1
Definition
A cyst is a pathological cavity in hard and soft tissues having fluid or semi-fluid or gaseous contents, that are not created by the accumulation of pus frequently, but not always lined by epithelium.
Continue reading
Thyroglossal duct cyst
A thyroglossal cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct.
Presentation
It usually presents as a midline neck lump (in the region of the hyoid bone) that is usually painless, smooth and cystic, if infected pain can occur. There may be difficulty breathing, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), and/or dyspepsia (discomfort in the upper abdomen), especially if the lump becomes large. Continue reading
Crowns for children
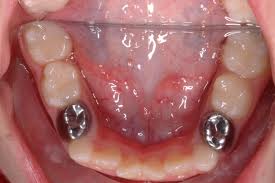 Intoduction to crowns for children
Intoduction to crowns for children
Just as we have crowns in adult dentition, so we have crowns for children. These crowns differ from those in adults in many ways, as will be discussed in the following sections. When your child has caries in his or her teeth, restorations with fillings such as composite or even amalgam is sufficient for small cavities, but if the cavity has become so large to an extent that normal restorations will be weak and easily fracture, a crown becomes the better option to protect the tooth from further damage. Continue reading