Definition
A cyst is a pathological cavity in hard and soft tissues having fluid or semi-fluid or gaseous contents, that are not created by the accumulation of pus frequently, but not always lined by epithelium.
Classification
They are divided into two main groups depending on the suspected origin of the lining epithelium.
1.Odontogenic cyst :the epithelial lining is derived from the epithelial residues of the tooth forming organ .They can be subdivided into developmental and inflammatory types depending on their etiology
2.Non-odontogenic cysts: the epithelial lining is derived from sources other than the tooth forming organ
Classification Of Jaw Cysts
(Based on WHO’s publication -1992- Pindborg, Kramer and Shear)
I) ODONTOGENIC CYSTS OF EPITHELIAL ORIGIN:
A) DEVELOPMENTAL
1. Odontogenic keratocyst (primordial cyst)
2. Dentigerous (follicular )cyst
3. Eruption cyst
4. Gingival cyst of infants , gingival cyst of adults
5. Lateral Periodontal Cyst
6. Botyroid odontogenic cyst
7. Calcifying odontogenic cyst
8. Glandular (sialo) odontogenic cyst
B) INFLAMMATORY
1. Radicular cyst
2. Residual cyst
3. Paradental cyst
4. Inflammatory collateral cyst
II) NON-ODONTOGENIC CYST
1. Nasopalatine duct cyst (incisive canal)
2. Globulomaxillary cyst
3. Nasolabial (nasoalveolar) cyst
4. Median mandibular cyst, median alveolar cyst,
III) Non-epithelial primary bone cysts
Solitary bone cyst (simple ,traumatic, haemorrhagic bone cyst)
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Odontogenic cysts
RADICULAR CYST
Periapical cyst, apical periodontal cyst, or dental cyst
A radicular cyst is a cyst that most likely results when rests of epithelial cells in the periodontal ligament are stimulated by inflammatory products from a nonvital tooth
CLINICAL FEATURES
They arise from nonvital teeth
Radicular cysts produce no symptoms unless secondary infection occurs.
A cyst that becomes large may cause swelling.
On palpation the swelling may feel bony and hard if the cortex is intact, crepitant as the bone thins, and rubbery and fluctuant if bone destruction has occurred.
Incidence : third to sixth decades and shows a slight male predominance.
Radiographic Features
Location: Apex of a nonvital tooth.
Occasionally it appears on the mesial or distal surface of a tooth root.
60% in the maxilla, incisors and canines.
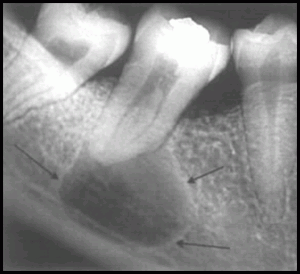
The epicenter of the lesion is in vicinity of the periapical region
of the involved tooth ,so the pulp chamber of the nonvital is
larger than normal.
PERIPHERY AND SHAPE:
well defined cortical border.
Round /ovoid radiolucency surrounds by a narrow radioopaque margin which extends from the lamina dura of the involved teeth. .
If the cyst becomes secondarily infected, the inflammatory reaction of the surrounding bone may result in destruction of the cortex or alteration of the cortex into a more sclerotic border.
INTERNAL STRUCTURE:
In most cases the internal structure of radicular cysts is radiolucent
Occasionally, dystrophic calcification may develop in long-standing cysts, appearing as sparsely distributed, small particulate radiopacities.
Effects on surrounding structures:
If a radicular cyst is large, displacement and resorption of the roots of adjacent teeth may occur.
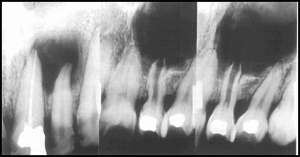
Radicular cyst healing after endodontic treatment, new bone is growing towards the center from periphery
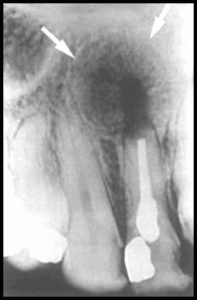
RESIDUAL CYST
Definition
A residual cyst is a cyst that develops after incomplete removal of the original cyst
Clinical Features
Asymptomatic and often is discovered on radiographic examination of an edentulous area.
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES
Location
More often in the mandible.
In the mandible the epicenter is always above the inferior alveolar nerve canal
Periphery and shape. cortical margin shape is oval or circular.
Internal structure. Â radiolucent
Effects on surrounding structures.
Residual cysts can cause tooth displacement or resorption. The outer cortical plates of the jaws may expand.
Differential Diagnosis
odontogenic keratocyst.
Stafne’s developmental salivary gland defect
DENTIGEROUS CYST
Synonym – Follicular cyst
Definition
A dentigerous cyst is a cyst that forms around the crown of an unerupted tooth. It begins when fluid accumulates in the layers of reduced enamel epithelium or between the epithelium and the crown of the unerupted tooth.
CLINICAL FEATURES
second most common type of cyst in the jaws.
They develop around the crown of an unerupted or supernumerary tooth.
The clinical examination reveals a missing tooth or teeth and possibly a hard swelling, occasionally resulting in facial asymmetry.
The patient typically has no pain or discomfort unless infected.
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES
Location
Above the crown of the involved tooth
Mandibular third molar or the maxillary canine,
An important diagnostic point is that this cyst attaches at the cementoenamel junction.
RELATIONSHIP TO TEETH
Tooth that may be displaced ,unerupted , or impacted.
The circumferential dentigerous cyst surrounds the entire crown but not the occlusal surface, so the tooth may erupt through the cyst as “through the hole in a doughnutâ€
The lateral dentigerous cyst occurs on one side of the involved tooth, which invariably is impacted or displaced, and the cyst may vary from small (1cm) to medium sized (2cm)
PERIPHERY AND SHAPE
well-defined cortex with a curved or circular outline.
Internal structure.
completely radiolucent except for the crown of the involved tooth
Effects on surrounding structures.
A dentigerous cyst has a propensity to displace and resorb adjacent teeth