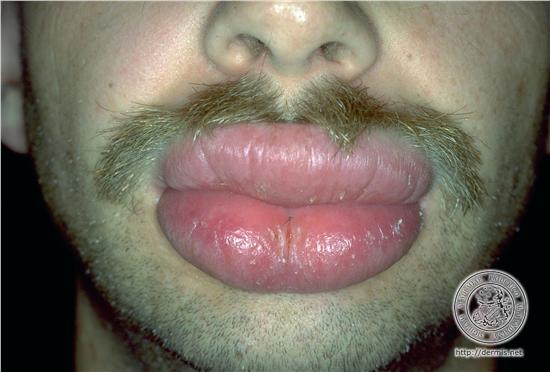
 Facial Edema (swelling)
Facial Edema (swelling)
Many surgical dental extractions results in extraction complications like facial edema or facial swelling after surgery. Routine extractions of a single tooth will probably result in swelling that the patient can see, whereas the tooth extraction of multiple impacted teeth with the reflections of soft tissue and removal of jaw bone may result in moderately large amounts of facial swelling. The facial swelling usually reaches its maximum size 24 to 48 hours after the surgical extraction procedure. The facial swelling begins to subside on the third or fourth day and is usually gone by the end of the first week. Increased swelling after the third day may indicate jaw infection at the surgical tooth extraction site.
Once the surgical tooth extraction is completed, the dental surgeon usually advices the patient to use ice packs to help minimize the swelling and make the patient feel more comfortable. The ice pack should not be placed directly on the skin, but rather a layer of dry cloth should be placed between the ice container and the tissue to prevent superficial tissue damage. An ice bag or a small bag of frozen peas should be kept on that local area of swelling for 20 minutes for 12 to 24 hours.
On the second day, neither ice or heat should be applied to the swollen area of the face.
On the third subsequent day, application of heat may help resolve the swelling more quickly. Heat sources such as hot water bottles and heating pads are recommended. Patients should be warned to avoid high level heat for long periods to keep from injuring the superficial layer of the skin.
Most important is that patients anticipate some amount of facial swelling. The facial swelling may tend to wax and wane, occurring more in the morning and less in the evening because of postural variance (sitting and lying down). Patients should not be concerned of frightened by the swelling, because it will resolve in a few days.
Trismus (Limitation in mouth opening)
The next tooth extraction complication is trismus . Trismus develops a s a result form the inflammation involving the muscles used for chewing food. Trismus may results from the multiple injections of local anesthetic give by the dental surgeon, especially if the injections penetrated the muscles. The muscle most likely to be involved is the medial pterygoid muscle , which is usually penetrated when giving a anesthetic block to the lower jaw.
Surgical tooth extraction of lower third molars results in some degree of trismus because the inflammatory response to the surgical procedure is sufficiently wide spread to involve several muscles of chewing.
Trismus is usually not severe and does not hamper the patients activity. However, to prevent alarm , patients should be warned that this phenomenon might occur.
 Prevention and recognition of an extraction infection
Prevention and recognition of an extraction infection
The principal way to prevent an extraction infection following routine extractions is for the surgeons to adhere carefully to the basic principles of surgery. These principles are to minimize tissue damage , remove source of infection and cleanse the wound.No other special measures must be taken with the average patient. However, some patients, especially those with depressed host-defense responses like diabetics or HIV patients may require antibiotics to prevent an infection form occurring. Antibiotics in these patients should be administered before the surgical tooth extraction procedure is started. Additional antibiotics after the surgery is no usually needed.
Extraction Infections in routine extractions are very unusual. The typical signs are development of a fever, increasing edema or worsening pain 3 to 4 days after surgery.Infected wounds usually look red, swollen and sometimes there will be pus discharged from the surgical tooth extraction area.
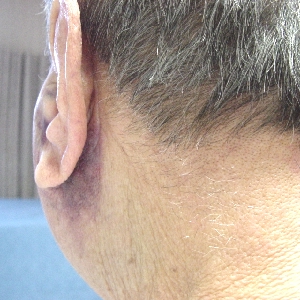 Ecchymosis (bruise)
Ecchymosis (bruise)
In some patients, blood oozes submucosally and subcutaneously, which appears as a bruise in the oral tissues or on the face. Blood in the superficial or sub mucosa part of the skin is known as ecchymosis. Ecchymosis is usually seen in older patients because of their decreased tissue tone, increase fragility of their blood vessels and weaker inter cells attachment. Ecchymosis is not dangerous and does not increase pain or infection. patients should however be warned that this event can occur. They should not become apprehensive when they wake up the next day and see bruising on their face.
So some instructions and warning will usually be given by the dental surgeon before any surgical tooth extraction procedure is done. Typically, the onset of ecchymosis is 2 to 4 days after surgery and usually resolves within 7 to 10 days.
Follow up visits to the dental surgeon
All pateints should ususally be given a follow up visit after any extraction to ensure that no post extraction complication arises. A follow up visit after a week of the surgical tooth extraction is usaully indicated. Sutures can also be removed during this appointment. However, if patients show signs of jaw infection, they should not hesisate to have an appointment immediately with their dental surgeon.
no coment! I will try to be in touch with you. Thanks
Pingback: Post Tooth Extraction | Pain Relief General Tips and Resources