Compomers†are recently introduced products marketed as a new class of dental materials. These materials are said to provide the combined benefits of composites (the “comp†in their name) and glass ionomers (“omerâ€). Based on a critical review of the literature, the author argues that “compomers†do not represent a new class of dental materials but are merely a marketing name given to a dental composite. Continue reading
Tag Archives: composite
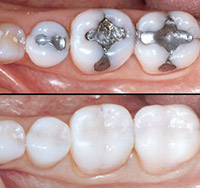
What is Composite/Tooth Coloured Filling Material?
Definition
By Anusavice
Composite – in material science, a solid formed from two or more distinct phases (e.g. particles in a metal phase) that have been combined to produce properties superior to or intermediate to those of the individual constituents
Dental composite is defined as a highly cross-linked polymeric material reinforced by a dispersion of amorphous silica, glass, crystalline, or organic resin filler particles and/or short fibers bonded to the matrix by a coupling agent
Understanding Dental Instruments ( Part 1 )
Once you enter the dental clinic, you will see a dental chair :
When you sit down in a dental chair, your eye first goes to the row of shiny, sharp instruments sitting in front of you. : Continue reading
Dental filling-What are the different options?
What is a dental filling?
A dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the physical integrity of the intended restorative material.
Dental fillings can be divided into three broad types: Continue reading
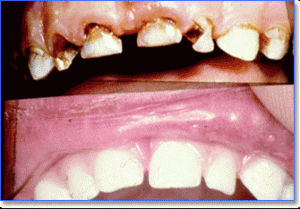
How to Replace Silver Dental Fillings
Transition from an old silver filling to a new one…
What is a silver dental filling?
“Silver†dental fillings or commonly known as amalgam fillings contain 50% mercury, silver, tin, zinc and copper. It is inexpensive, easy to use and manipulate during placement into cavities as it is soft, moisture tolerant, less technique sensitive and forms a hard material on set. Amalgam has greater longevity as long as 10 years or more compared to other restorative materials and is wear resistant. Amalgam is condensed and packed into prepared cavities. They lack the bonding mechanism when compared to bonded fillings which restore 85% of strength that the tooth had before the first filling. Continue reading
Dental Bonding
Dental Bonding or bonding teeth is a procedure whereby a material resembling natural teeth is joined onto the tooth surface. This is done to improve the appearance and function of the tooth. It is commonly used in fillings for decayed teeth. There are two types of Dental Bonding. Direct Dental Bonding and Indirect Dental Bonding. For Direct Bonding, the Dental Bonding agents which are used include composite (resins), GIC (glass ionomer cements) and ready made composite veneers. This procedure can usually be completed within 30 -45 minutes. In the case of Indirect Bonding, the Dental Bonding Agents used here would be porcelain veneers. Multiple visits are usually needed for this procedure as extra fabrication time in the lab is needed to custom make these porcelain veneers. Continue reading