Causes of gum bleeding
1.     Gum diseases
A. Gingivitis.
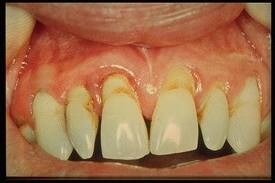
Gingivitis comes from the word “gingiva†which means gums and “-itis†which means inflammation, hence gingivitis means inflammation of the gums. Poor tooth brushing technique or the lack of it leads to accumulation of plaque around the teeth, and eventually leads to gum diseases such as gingivitis. You should suspect gingivitis when you have other symptoms such as :
i)Â Â Â Â Â Â altered appearance of your gums (deep red in colour, soft and swollen appearance, loss of a scalloped and knife-edge shape)
ii)Â Â Â Â discomfort and pain
iii)Â Â Â unpleasant taste
iv) Â Â bad breath or halitosis
B. Periodontitis
If gingivitis is not treated, the condition will worsen and gradually lead to periodontitis, which is infection and inflammation of the supporting tissues of the teeth, which includes the gums, the fibres attaching the tooth to its socket (the periodontal ligament), the cementum (the outermost layer of the root of the tooth), and the bone which holds the tooth in its place. You should suspect periodontitis if you have other symptoms such as:
i)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Pocket formations (a pocket formed by the gums and the tooth)
ii)                 Gingival recession– the gum line recedes slowly revealing more of the tooth’s root surface,
iii)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Tooth or teeth mobile or loose
iv)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Tooth or teeth appears to have drifted
v)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Halitosis and foul taste in mouth
 2.     Canker sores
Canker sores, or mouth ulcers can appear anywhere in the mouth and are usually painful. When they appear on the gums, that area becomes sore and is associated with gum bleeding. Canker sores often heal with time.
 3.     Chemotherapy
Patients undergoing chemotherapy may experience side effects such as stomatitis and dry mouth, which leads to occurrences of mouth ulcers and infection on the gums and in the mouth.
4.     Smoking
People who smoke have a higher tendency to develop gum diseasessuch as ginigivitis and periodontitis.
5.     Trauma-brushing too hard, wrong technique or flossing
As important as it is to brush and floss your teeth daily, an emphasis should equally be placed on the correct technique in carrying out these tasks, as the wrong technique may be more detrimental to the health of your teeth and gums as compared to not doing it at all. For instance, if you brush your teeth with too vigorously and with the wrong stroke of motion (eg horizontal strokes instead of the recommended bass technique), you may be gradually wearing away tooth substance and induce trauma to the gums, which leads to gum bleeding and gum recession, which is aesthetically unpleasant.
Also, for those who are not accustomed to the habit of flossing, when you first start out on this practice, you may experience bleeding from your gums where the floss “strikes†your gums as you floss. This is a normal phenomenon and you should not worry about this. As you develop the habit of flossing daily, your gums will stop bleeding.
6.     Pregnancy (hormones)
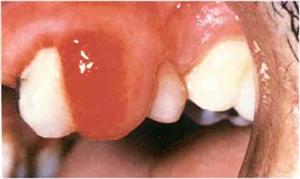
There is increased level of sex hormones during pregnancy, namely oestrogen and progesterone. Progesterone is the one responsible for increased vascularity and permeability of gingival blood vessels. As a result, the gums may appear bright red, swollen and sensitive, and may even be spontaneous bleeding, increase in exudates and mobility. This is also known as “pregnancy gingivitisâ€. It may even result in pregnancy epulis, also known as pyogenic granuloma of pregnancy, which essentially is a soft swelling, deep red in color, and bleeds easily, which causes patient concern. This epulis may appear anytime during pregnancy but usually occurs after the 3rd month. It usually regresses partially or completely after parturition. These conditions are not imminent of pregnancy; rather, they are the aggravated response to plaque and other plaque-inducing factors because of the hormonal changes in the body. Thus, maintaining good dental hygiene throughout pregnancy can help reduce inflammation of the gums.
7.     Iatrogenic (dentist is the cause)-following dental scaling
Sometimes you may have gum bleeding for days following an appointment with a dentist during which scaling was done. This could have been because you had poor gum health previously, and removal of plaque and calculus left a relatively “open†gingival sulcus (the pocket between teeth and your gums accessible by a blunt dental probe) from which bleeding can occur. Another reason why you’re bleeding could also be that the dentist could have accidentally caused too much trauma to your gums while scaling.
8.     Bleeding problems & other disorders
Sometimes bleeding gums is a sign of other systemic problems such as leukemia and bleeding and platelet disorders.