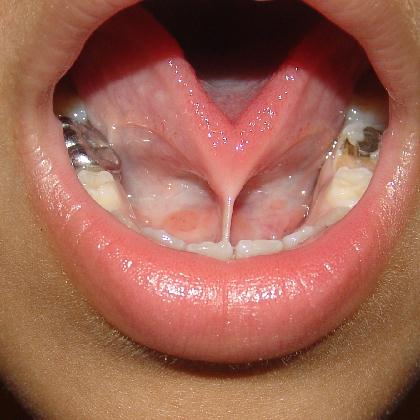
 Tongue-tie is also known as Ankyloglossia. It is a condition in which the lingual frenulum is either too short or forwardly placed limiting the movement of the tongue. Reports of partial tongue-tie affecting several generations., suggest a possible genetic basis for the minor variation in the attachment of genioglossus muscle. It may be traumatic or congenital.
Tongue-tie is also known as Ankyloglossia. It is a condition in which the lingual frenulum is either too short or forwardly placed limiting the movement of the tongue. Reports of partial tongue-tie affecting several generations., suggest a possible genetic basis for the minor variation in the attachment of genioglossus muscle. It may be traumatic or congenital.
 Types :
Complete – Fusion of tongue and the floor of the mouth
Partial – Short Lingual Frenum
Clinical Features :
- Symptoms
- It may limit the movement of your tongue. In extreme cases of ankyloglossia, nursing and feeding problems can occur.
- Recurrent tongue biting, poor sucking and inability to chew some food.
- It was felt that tongue-tie is associated with speech abnormalities, especially lisping and inability to pronounce certain sounds and words like t,d,n,l,as,ta,te,time and etc.
- Signs
- When there is an attempt to stick your tongue out, there may be a V-shaped notch at the tip
- Physical examination will easily demonstrate the short and forwardly placed lingual frenulum
- Patients have midline lower jaw gap/diastema and  inability to clean the teeth and lick the lips with tongue.
- Syndromes associated : ankyloglossum superious sydrome, Rainbows’s Syndrome, Fraser’s Syndrome and orofacial digital syndrome.
How to diagnose if your baby has tongue tie?
Sucking blisters: these are a tell-tale sign that your baby may have a tongue tie. With a tongue tie the baby has to hold on tight with her lips, thus a blister may appear. Sometimes the lips appear white after feeding.
Fatigue: when the tongue is not able to perform its job well, the baby will use smaller, less powerful muscles to do this job. These babies tend to get tired quickly. You may notice small quivers of your baby’s chin- a sign of overtaxed muscles. Think about having to perform all of the jobs your arms and fingers normally do together with just your fingers. How long would you last?
Management
- Physician education, parental education and reassurance should be given to the patient
- Surgery – indication for surgery that is frenectomy are as follows :
- If complete fusion of the tongue is present then it requires surgery.
- When nursing and feeding becomes a problem, surgery is needed
- Children between 2-4 years , with poor developement of speech and anxious parents desire for the necessary treatment.
- In cases where tongue tie has recurred after snipping
 Lingual Frenectomy
This procedure is performed when there is ankyloglossia (tongue-tie) or when there is high lingual frenal attachment. This attachment binds the tongue to the lingual surface of the alveolar ridge. Lingual frenectomy is perfomed even when prosthesis is not requires as it interferes with normal speech. Once the teeth are lost, it disturbs the stability of the denture each and everytime when the tongue is moved.
Technique Â
- Nerve block anesthesia of inferior alveolar nerve and lingual nerve is preferred. Local infiltration might disturb the normal anatomy of the region and interfere with accurate incision.
- Once the anaesthesia is secured, a 3-0 silk suture is passed through the midline of the tongue around 2 cm from the tip
- This is done to hold the tongue up so that the frenum becomes taut.
- Using a sharp scissors, a cut is made 1 to 2 mm midway between the tip of the tongue and the lingual surface of the mandible.
- The cut is made in such a way that the blades of the scissors are parallel to the floor of the mouth.
- Care should be taken not to injure the submandibular duct, salivary caruncle and the blood vessels in the floor of the mouth.
- In certain cases, genioglossus muscle should also be dissected in addition to lingual frenum.
- The wound margins are undermined, approximated and closed without tension.
Cleft Tongue
- It is also called as bifid tongue.
- It is a condition in which there is cleavage of the tongue due to lack of fusion of the lateral halves.
- It results due to incomplete merging and failure of the groove obliteration by underlying mesenchymal proliferation.
- It is completely bifid or cleft tongue is rare.
- It is due to lack of merging  of lateral swellings of the organs.
- Food debris and microorganisms may collect in the base of the cleft and causes irritation
- It is seen with oral-facial-digital syndrome, with thick fibrous bands in lower anterior mucobuccal fold, which eliminate the sulcus and is associated with clefting of hypoplastic mandibular alveolar process
Ankyloglossum Superius Syndrome
It is characterized by the attachment of the tongue to the hard palate and by limb malformations
- A genetic disorder – it is most important cause of this syndrome
- Intrauterine- It also causes this syndrome
- It is a very rare disorder and is associated with jejunal and ileal atresias
- Difficulties in speech and mastication as well as swallowing
Management
Surgical separation of the tongue from palate