Saliva has many different functions; to name a few, digestion, lubrication, to help you taste food, to protect your teeth from tooth decay, helping you swallow food, and protection your mouth from infection. It is produced by the many salivary glands in out mouth. There are 3 pairs of major salivary glands (the parotid glands, the submandibular glands and the sublingual glands, one of each on each side of the face) and over 600 minor salivary glands. These glands are connected by a duct and open into the mouth via small orifices. Sometimes we take saliva for granted such that we don’t realize how important it is until we’ve lost it. A normal person produces 4-6 cups of saliva daily. If the production decreases, he or she will have symptoms of “dry mouthâ€, or “xerostomiaâ€, resulting in a great discomfort and inconvenience. It is a common phenomenon especially among middle aged and elderly women.
What causes dry mouth?
-
Side effect of certain conditions or diseases.
Dry mouth can be a side effect of medical conditions, including Sjogren’s syndrome, depression, renal disease, HIV or AIDS, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus, anemia, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, stroke, mumps, hypertension, Parkinson’s disease.
2. Medication
Some medications have side effects causing dry mouth. These include drugs used to treat depression, allergies, anxiety, pain, and colds (antihistamines and decongestants), obesity, epilepsy,diarrhea, nausea, mental disorders, hypertension (diuretics), acne, asthma (certain bronchodilators), urinary incontinence (inability to contain urine), and Parkinson’s disease. Dry mouth can also be a side effect of muscle relaxants and sedatives.
3. Side effect of certain medical treatments.
Damage to the salivary glands, for example, from radiation to the head and neck and chemotherapy treatments for cancer, can decrease the production of saliva by the salivary glands
4. Nerve damage.
Dry mouth can be a result of damage to the facial nerve (the seventh cranial nerve) from an injury or surgery on the head and neck area.
5. Dehydration
Conditions that lead to dehydration, such as vomiting, diarrhea, fever, excessive sweating, burns and blood loss can cause dry mouth.
6. Surgical removal of the salivary glands.
Surgical removal of the salivary gland is usually carried out when the gland is involved by a tumour.
7. Developmental defects:
some people are born with missing salivary glands (aplasia) or obstruction of the salivary duct (atresia).
8. Lifestyle and habits.
Smoking or chewing tobacco can reduce saliva production and aggravate dry mouth. Habits such as subconsciously breathing with your mouth open over a long period of time (for example, during sleeping) can also contribute to the problem. Drinking beverages containing caffeine like tea, coffee, and soft drinks, alcohol consumption or using alcohol-based mouthwash can also cause dry mouth.
Symptoms of dry mouth
1. Constant stickiness and dryness of mouth
2. Frequent thirst
3. Burning sensation of the tongue
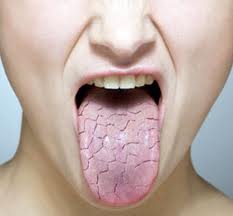
4. Dry, red and fissured tongue
5. Hoarseness
6. Difficulty in chewing, swallowing and speaking
7. Mouth sores
8. Bad breath (halitosis)
9. Dry, cracked lips

Drink lots of water!
How to treat dry mouth?
Firstly, if you have dry mouth, the cause should be identified. Treatment can then be based on it. For example, if it is due to the side effects of the medication you are prescribed, you can consult your doctor and request for a change of drug. If it is due to your habit of breathing through the mouth, smoking, or frequent alcohol intake, you should stop the habit.
Here are some other steps that may alleviate the symptoms of dry mouth:
1. Frequent consumption of water or sugar-free juices
2. Protect your lips using lip balms that contain aloe vera or vitamin E.
3. Protect your teeth by application of fluoride or using fluoride toothpaste
4. Avoid using alcohol-cased mouthwash
5. Use a humidifier to add moisture to the room
6. Sugar-free chewing gum- chewing will help to stimulate more production of saliva
7. Prescription of salivary substitutes, such as pilocarpine, or artificial saliva.
What if dry mouth is left untreated?
1. Under such a condition, the mouth susceptible to infection especially by fungus, and also bacteria.
2. Saliva is also responsible for protecting teeth against caries attack, hence the lack of it may result in a high caries rate. If you have dry mouth, you should protect your teeth through application of fluoride or mouthwash, and reduce sugary diet intake.
3. Dry mouth can alter a person’s dietary choice, resulting in a compromised nutritional state.
4. Denture-wearers will experience great discomfort if they have a dry mouth. Furthermore, they will be more susceptible to fungal infection which will then lead to complications such as denture stomatitis.