Amalgam was first introduced in United States during 1833. It is then used widely as dental filling material over the years because of its strength, durability and low cost (especially for posterior teeth). It is now discontinued or banned in certain countries such as Norway, Sweden, Denmark because of its known biological effects on human body. Amalgam is made of metals such as Silver, Tin, Copper, Zinc and Mercury. 50% of amalgam is made of mercury and they are then mixed to form a hard material which has silvery grey appearance through a process which is known as amalgamation. Patients are exposed to high dose of mercury during the process of placing and removal of amalgam restoration. Continue reading
Tag Archives: dental amalgams
Composite vs Amalgam
Composite resin and amalgam are the most commonly used filling materials in dentistry. Throughout the years, the content of both materials have been modified to improve the quality of the fillings.
Dental composite resins are types of synthetic resins. A composite material is a product which consists of two distinct phases normally formed by blending together components having different structures and properties.The purpose of this is to produce a material having properties which could not be achieved from any of the individual components alone. The two main components of composite filling materials are resin phase and the reinforcing filler. The resin gives the material the ability to be moulded at ambient temperature and polymerization achieved in a short time.Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, aesthetic, and insensitive to dehydration and were inexpensive. It is easy to manipulate them as well. Composite resins are most commonly composed of Bis-GMA monomers, a filler material such as silica and in most current applications, a photoinitiator. Dimethacrylates are also commonly added to achieve certain physical properties such as flowability. Further modification of its physical properties is achieved by changing the concentrations of each constituent.Unlike amalgam which essentially just fills a hole, composite cavity restorations when used with dentine and enamel bonding techniques restore the tooth back to near its original physical integrity.
The main advantage of dental composite over amalgam is improved aesthetics. Composite is a tooth coloured material and it comes in a wide range of tooth colours allowing near invisible restoration of teeth. Composite is bonded to the tooth with the use of dentine bonding agent. This strengthens the tooth structure. Unlike amalgam, there is no need to create retentive features which destroys healthy tooth structure because composite bonds to tooth chemically. Therefore, using composite material as filling is proven more conservative and less tooth preparation is needed. Continue reading
When to get a dental filling?
What is a  dental filling?
A tooth consists of enamel,dentine, pulp and cementum. Enamel is the outermost layer which forms the crown of a tooth. Tooth surface is covered by a bacterial biofilm,known as plaque. The bacteria metabolizes sugar and releases acid which destroys the enamel. This process is called decay or dental caries. When oral hygiene is inadequate, dental decay progresses into the dentine layer and in later stage, into the pulp. Decayed tooth is weak and brittle, thus it becomes soft, forming what is called cavity. A tooth damaged by decay needs to be filled to restore its normal function, shape and strength. Continue reading
Are Mercury Dental Fillings Safe?
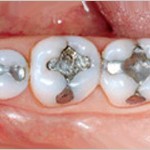 Mercury dental filling, or best known as dental amalgam is an alloy of silver, tin, mercury, and copper as it’s constituent. The term amalgam is also used as a synonym by the dental profession. Among all, silver and tin have the highest composition within an amalgam.
Mercury dental filling, or best known as dental amalgam is an alloy of silver, tin, mercury, and copper as it’s constituent. The term amalgam is also used as a synonym by the dental profession. Among all, silver and tin have the highest composition within an amalgam.
The use of mercury in the oral environment has raised concerns regarding safety. Currently, several countries have banned the use of dental amalgam because of environment concerns, as well as alleged side effects that may be sustained by patients who receive dental amalgam restorations.