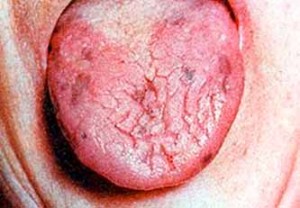
Pigmentation in mouth, which ranges from brown to black, may be due to superficial (extrinsic) or deep (intrinsic) causes. They may result from the localization of exogenous substances on or within the mucosa, or may be due to deposition in the tissues of endogenous pigments (for example substances produced by the body), of which melanin is the most common. Continue reading
Category Archives: Oral Care
Why Are My Teeth Discolored? Part 2
Continued from Part 1
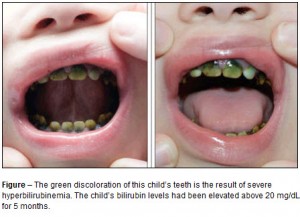
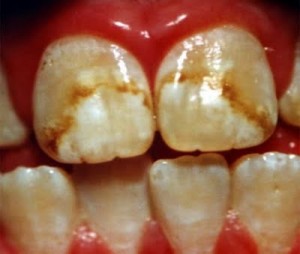
Incorporation of pigments into the dental hard tissues during their formation
This occurs in congenital disorders associated with hyperbilirubinemia, congenital porphyria and tetracycline pigmentation. Continue reading
Why Are My Teeth Discolored? Part 1
Our teeth can discolor for various reasons. From dietary stains to in-born conditions, many factors can play a role in making our teeth not as perfect as we want it to be. Therefore it is important that normal variation in the color of teeth be distinguished from tooth discoloration due to disease origin (pathological). Continue reading
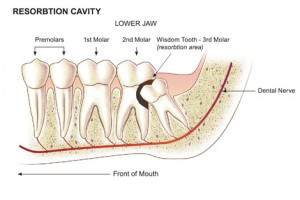
Tooth Resorption Part 2
Continued from Part 1
Pressure or mechanical resorption
Root resorption associated with pressure or mechanical stimulation may be seen in individuals undergoing orthodontic treatment and can be caused by the application of excessive force. It occurs in the apical region and the resorbed area undergoes repair and remodeling when the cause is removed. It is possible that excess force could cause an aseptic death of the periodontal ligament, followed by inflammation. Pressure may also be a factor in root resorption associated with tumors or, occasionally, cysts involving the roots of teeth. Continue reading
Tooth Resorption Part 1
The natural shedding of baby teeth follows the progressive resorption of the roots by cells resembling osteoclasts (Cells that functions in the breakdown and resorption of bone tissue). This physiological resorption may be an inherent developmental process or it may be related to pressure from the permanent successor against the overlying bone or tooth. Continue reading
Tooth Pain After Filling Part 2
Continued from Part 1
Teeth grinding habit
Clenching and grinding or bruxing of the teeth can cause additional occlusal load or stress to the teeth and may lead to fracture of a restored tooth, causing pain. Continue reading
Tooth Pain After Filling Part 1
Teeth fillings are placed to restore a tooth back to its functional or aesthetic state. Besides tooth decay, tooth filling is also done for cracked and broken tooth, worn teeth, bruxism (teeth grinding) and other reasons. However the problem of tooth pain after filling is done can be quite common. Continue reading
Sore tongue
Sore tongue medically known as stomatitis is a very common symptom. Most of the doctors routinely prescribe B-complex tablets, terming it B-complex deficiency. In fact in many instances it is not so. Painful tongue is a common problem. Many of us experience a sore tongue from time to time. But what should you do about it if it affects you. Continue reading
Cystic hygroma
A cystic hygroma is a growth that often occurs in the head and neck area. It is a birth defect and is the most common form of lymphangioma. It contains large cyst like cavities containing watery fluid. Microscopically cystic hygroma consists of multiple locules filled with lymph. In the depth the locules are quite big but they decrease in size towards the surface. Continue reading
Tooth erosion
Acid erosion, also known as dental erosion, is the irreversible loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution by acids not of bacterial origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic disease of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognised as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to fruit juices, because they tend to be seen as healthy. Erosion is found initially in the enamel and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin. Continue reading