Continued from Part 1
The new guidelines are aimed at individuals who would have the greatest risk of a bad outcome if they developed a heart infection.
Antibiotics cover prior to a dental procedure is advised for individuals with: Continue reading
Continued from Part 1
The new guidelines are aimed at individuals who would have the greatest risk of a bad outcome if they developed a heart infection.
Antibiotics cover prior to a dental procedure is advised for individuals with: Continue reading
Prophylaxis is the prevention of an occurrence. In surgery this is usually infection or thromboembolism (Occlusion of a blood vessel by an embolus that has broken away from a blood clot formed within a blood vessel). Prophylaxis used to prevent the occurrence of bacterial infection is quite different from treating an established infection. Continue reading
Midface dysplasia is a cardinal characteristic of persons with Down Syndrome (DS). Nose malformations including a flat broad bridge of the nose has been reported in 59-78% of these individuals. Ear malformations, including “lop” ears, low-set ears and ears with a flat or absent helix have been reported in 54%. Eye malformations are common. Epicanthal folds with slanting almond-shaped eyes (narrow palpebral tissue slanting toward the midline), which was responsible for the term mongoloid, are reported in 78%. Strabismus (cross eyes) is reported in 14-54% and nystagmus (constant involuntary cyclical movement of the eyeballs) and refractive errors are also common. The majority of persons with Down Syndrome exhibit brachycephaly (broad, short head) and lack of supraorbital ridges and hypotelerism (secondary to hypoplasia of the central face) are common findings. Absence of frontal sinuses and absent or reduced maxillary sinuses have been reported. Nasal septum or nasal conchal deviations are often observed which can produce a partially obstructed or narrow air passage and can contribute to the problem of mouth breathing. Continue reading
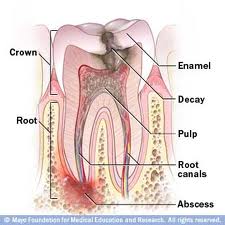 Having a tooth abscess is literally a pain therefore one would not have second thoughts in pulling the miserable tooth out. However tooth extraction may not be the only way out of the pain. Continue reading
Having a tooth abscess is literally a pain therefore one would not have second thoughts in pulling the miserable tooth out. However tooth extraction may not be the only way out of the pain. Continue reading
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) is the term for non-specific diagnosis that represents a group of often painful and/or dysfunctional conditions involving the muscles of mastication or the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) or both. Continue reading
Continued from Part 1
The glandular odontogenic cyst is a rare, developmental odontogenic cyst. Most common site of occurrence is the front region of the lower jaw where they present as slow-growing, painless swellings. The cyst has a potentially aggressive, locally invasive nature and a tendency to recur. Continue reading
Swellings and lumps in the mouth are common. Some may be just anatomical structures in the mouth while some may be of other origin, including jaw cysts. Continue reading
A cyst is defined as a pathological cavity having fluid or semi-fluid contents, which has not been created by the accumulation of pus. Cysts of the jaws are more common than in any other bone, and the majority are lined wholly or in part by epithelium. Continue reading
 What is a dry socket?
What is a dry socket?Dry socket or also known as alveolar osteitis is a common complication occurring after the extraction of a permanent teeth especially the lower wisdom teeth. The term ‘alveolar’ refers to the jawbone that supports teeth while ‘osteitis’ refers to the inflammation of the bone associated with the extraction socket.
The condition has generally been characterized by degraded or delayed healing associated with breakdown or dislodgement of the blood clot in the extraction socket. It is usually accompanied by persistent, radiating pain in and around the extraction site within a few days after extraction that is not easily relieved by pain killers. The premature loss or breakdown of the blood clot is accompanied by exposure of the underlying bone. Continue reading
Autism affects about 1 or 2 people in every thousand and is three to four times more common in boys than girls. Dental management for children with autism will vary from normal due to their special condition. Continue reading