How Will You Know If You Are Suffering From Trigeminal Neuralgia or Toothache?
Â
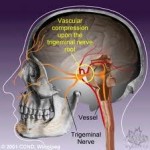
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition affecting the trigeminal nerve, which carries the sensation, touch, pain, and temperature from the face to the brains. It is on either side of the face and consist of three branches hence the name. The maxillary and mandibular branch is commonly affected around the cheeks and jaw. Also known as tic douloureux, occurs when a blood vessel (artery or vein) impinges on this nerve at the base of the brain under pressure leading to disruption of its function. The superior cerebellar artery is the most common vessel causing neurovascular compression.
Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Short, mild attacks that progress to long, severe, frequent ones over time
- Period of shooting, stabbing pain like an electric shock
- Spontaneous pain on shaving, applying make-up, tooth brushing, eating, touching the face, talking or even smiling by stimulating the “trigger-zonesâ€
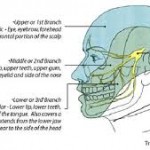
- Pain in areas supplied by trigeminal nerve ( cheeks, lips, teeth, gums, jaw, lower eyelid, side of nose and forehead)
- Pain on one side of the face at a time with pain-free intervals
- Pain on a particular region or over a wide-spread area
Â
Causes of TN
TN occurs as results of aging, multiple sclerosis particularly if pain involves both sides of the face, eyes, forehead and over a short time period. Other causes include damage to the myelin sheath of a nerve, aneurysm or due to a tumor. This causes numbness over the face and weakness of the facial muscles. Women are affected more than men usually above 50 years but can also occur in the young. A neurological examination by touching and examining parts of the face can determine the site of pain or MRI of the head can show if multiple sclerosis is the cause of TN. Atypical TN will have a prominent, constant, severe burning or boring pain superimposed with typical TN symptoms. It may be a severe form or progressed typical TN. Those affected have sleep deprivation and live in fear of the next attack. This interferes with eating, can lead to anxiety, depression, serious malnutrition and weight loss.
Treatment and Management of TN
Patients suffering from this disorder respond well to carbamazepine (anticonvulsant drug). They can ease the pain in 1-2 days with a low dose which then increases depending on the pain. The dose can be decreased gradually and stopped if possible when pain comes to a halt. Phenytoin and gabapentin can be prescribed with the aim to block the signals being transmitted to the brains. Baclofen (anti-spasmodic agent) can also be given, they act as muscle relaxants. The side effects include drowsiness, nausea, double vision and confusion. An alcohol injection may give a temporary relief but infections and damage to nearby nerves can occur. If severe, surgery is the mode of treatment with many different options available. The goal of surgery is to stop the compression of blood vessel on the nerve or to damage the nerve to keep it from malfunctioning. Acupuncture, biofeedback and relaxation techniques are other complementary therapies which help to decrease pain. You may need to change treatment or repeat some treatments over time.

Toothache
On the other hand, toothache can occur due to
- Infections of the ear or sinus problems especially when pain is limited to the upper teeth and several teeth are affected at a time, may also involve the jaw
- Recent dental work (restoration or scaling)Â result in teeth sensitive to temperature changes over a period of time
- Bruxism (teeth grinding) or temperomandibular joint associated problems, injury, arthritis, jaw muscle fatigue may cause a tooth to be sensitive or experience a toothache
- Abscess as a result of death of pulp tissue which then becomes infected and spreads to gum and bone which interferes with daily function or disturbs your sleep at night
- Gum disease with an early symptom of bleeding without pain, an advanced lesion may have deep pockets, bone destruction surrounding teeth and even loss of otherwise healthy teeth
- Poor dental hygiene as a result of not brushing or flossing teeth regularly
- Poor diet due to eating too many refined sugars or flours, sugary drink and candies frequently
- Deep cavity, loose filling, impacted teeth, exposed tooth root (recession) or cracked tooth (tooth fracture) emitting a sharp pain on biting
- Transferred pain from heart problems such as a heart attack or angina not responding to home or dental treatment
The severity of a toothache can range from chronic and mild to sharp and excruciating pain. Ibuprofen is the most effective analgesic that relieves a pain accompanying a toothache. The pain maybe aggravated by chewing, biting or after consuming hot and cold drinks. A thorough oral examination and additional aid of dental x-rays will help determine the origin of pain either teeth or jaws and the underlying cause.
Treatment varies depends on the cause of a toothache from filling a cavity, root canal treatment, placing a crown, night guards to help control brusixm, abscess drainage with antibiotic course, scaling, root planning, curettage, surgical removal of impacted teeth, improving oral hygiene and proper diet.