Overview of sarcoidosis disease
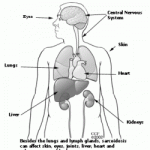
Sarcoidosis is a multi-system (affects all systems of the body) granulomatous disease . A granuloma is a localized nodular inflammation of our immune cells which fuse together to form larger cells and finally form large nodules in our body.
This disease usually affects the lungs , but it can affect any other organs. Skin lesions are also common.
Currently there is no known cause for the sarcoidosis disease. It affects young adults and equally occurs in both male and female.
Sarcoidosis Symptoms
Dental symptoms :
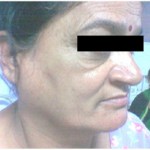
- There is a non- symptomatic enlargement of the major salivary glands in 6% of the patients. Patients with sarcoidosis can have sudden enlargement at the side of the face or at the bottom of the chin. Locations where the salivary glands are situated.
- Xerostomia is a condition of dry mouth. Dry mouth happens when patients take certain medications, but in this case it is not cause by any medication.
- Gingival enlargement or gum enlargement. This can be a late or early feature of sarcoidosis disease.
- May be associated with Sjogren’s disease.
- Swelling of the lymph nodes of the face and neck.
Other symptoms :
- patients complain of fatigue (tiredness) even after waking up from a full night of sleep.
- low level of energy
- joint pain (athralgia)
- dry eyes, blurred vision
- shortness of breathe due to respiratory impairment
- coughing
- affects the heart, may cause sudden cardiac arrest (heart failure)
- diffuse patchy hair loss
- inflammation of the eye
- weight loss and fever
- enlargement of the spleen and liver
Sarcoidosis Treatment
Between 35 to 70% of patients do not require therapy. However, steroids ,most commonly prednisolone, has been the standard treatment. In some patients, this treatment can slow or reverse the course of the disease and some do not respond to steroid therapy. The use of steroids in mild disease is usually not recommended because in many cases the sarcoidosis disease can slowly go away by itself. Additionally, steroids have many side effects and their use is generally limited to severe, progressive, or life threatening diseases.
Another form of treatment is vitamin D regulation. This is because it has been said that vitamin D dis-regulation can be a cause for this sarcoidosis disease to occur.
In cases of salivary gland enlargement, it may take up to to 3 years for the salivary gland to return back to normal size.
Sarcoidosis Causes
There is currently no known causes of sarcoidosis disease. However there has been speculation, some researchers say that sarcoidosis can be caused by an allergic reaction. Where else , some others say that it is caused by an immune dysfunction of our body.
Sarcoidosis Diagnosis and Test
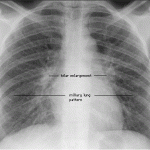
- routine chest x ray, nodules can be seen in sarcoidosis disease
Sarcoidosis research has shown that sarcoidosis disease can affect multiple organ systems, follow-up on a patient with sarcoidosis should always include the following:
- electrocardiogram, to test the function of the heart
- ocular examination by an ophthalmologist, to see the function of the eyes
- liver function test
- serum calcium and 24-hour urine calcium, to test the function of the kidneys
- Unbalanced level of thyroid hormones are usually seen in female patients suffering form sarcoidosis disease, therefore patients usually go for a thyroid marker test, which test the level of the t3 and t4 thyroid hormones.
- FNAC (fine needle aspiration count) a sample of the salivary gland tissues are taken with FNAC method to diagnose and confirm the sarcoidosis disease
Sarcoidosis Prognosis
The disease can disappear spontaneously or become worse altogether. In some patients, it can progress to fibrosis of the heart (heart tissue hardens up) and that will lead to death. Approximately half of the cases resolve by itself or can be cured within 1 to 3 years and most within 5 years. however, some can last for more than 10 years. Patients with sarcoidosis tend to be more prone at developing cancer, highest particularly for lung cancer and any other organs affected by this sarcoidosis disease. Non- Hodgkin lymphomas are also know to develop. However, as mentioned above, more than 35% to 70% of patients do not require treatment as the disease goes away by itself. As an overall, the prognosis is quite good.
Complications of sarcoidosis disease
- pulmonary fibrosis (fibrosis of the heart) leading to heart failure
- The effect on the lungs will cause breathing difficulties.
- Blurred vision or very dry eyes, leading to blindness.
- Dry mouth, gum enlargement, salivary gland swelling.
When to contact a doctor
most symptoms are mild and overlooked most of the time . However, if it all adds up, please see a physician immediately
- sudden swelling of salivary glands
- swollen gum’s
- dry mouth
- dry eyes, blurred vision
- difficulty in breathing